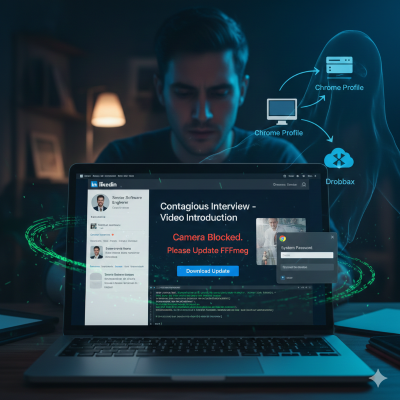
Weekly Roundup
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 12/29/25
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: The CyberBunker’s underground facility in Germany is up for sale Originally purchased in
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 12/15/25
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: Twins with hacking history charged in insider data breach affecting multiple federal agencies
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 12/8/25
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: Block all AI browsers for the foreseeable future: Gartner Based on the advisory
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 12/1/25
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: North Korea lures engineers to rent identities in fake IT worker scheme This