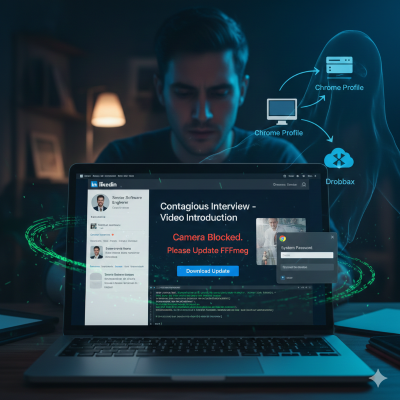
ransomware
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 12/29/25
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: The CyberBunker’s underground facility in Germany is up for sale Originally purchased in
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 9/29/25
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: US Auto Insurance Platform ClaimPix Leaked 10.7TB of Records Online This colossal data
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 9/15/25
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: Former FinWise employee may have accessed nearly 700K customer records The data breach at
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 9/8/25
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: Hackers Weaponize Amazon Simple Email Service to Send 50,000+ Malicious Emails Per Day A