Threat Intelligence
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 2/2/26
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: Coinbase confirms insider breach linked to leaked support tool screenshots This analysis examines
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 1/12/26
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: California bans data broker reselling health data of millions The recent enforcement action
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 1/5/26
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: China Hacked Email Systems Used by US Congressional Staff, New Report This article
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 12/1/25
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: North Korea lures engineers to rent identities in fake IT worker scheme This
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 10/13/25
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: Satellites found exposing unencrypted data, including phone calls and some military comms This
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 10/6/25
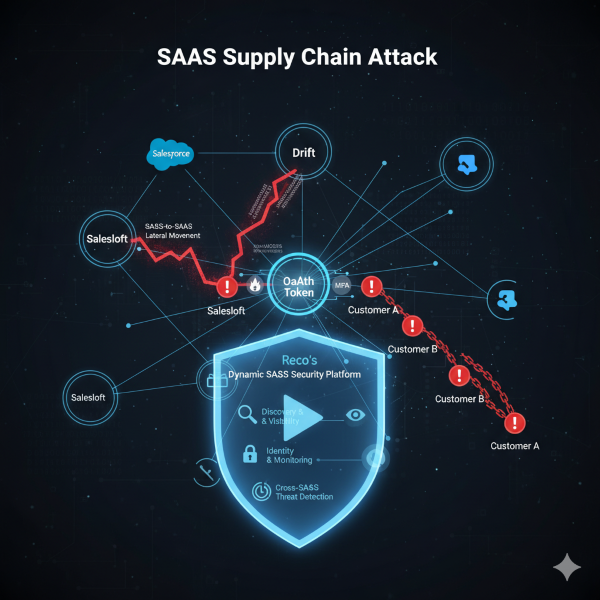
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: The Salesloft-Drift Breach: Analyzing the Biggest SaaS Breach of 2025 Analysis of The
-
What’s New in Cybersecurity This Week: Projects, Videos, Articles & Podcasts I’m Following – 8/11/25
Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week. Featured Analysis Featured article analysis: New York claims Zelle’s shoddy security enabled a billion dollars in scams The